
Mongol herdsman
Hunting wild animals
The first people moved into Central Asia about 50,000 BC. They were probably following the big animals that they hunted for food and leather skins – the wild aurochs and the wild horse. The great grasslands of Central Asia were a good place for aurochs and horses, because they eat grass.
What is an aurochs?
The evolution of horses
Herding cattle and horses
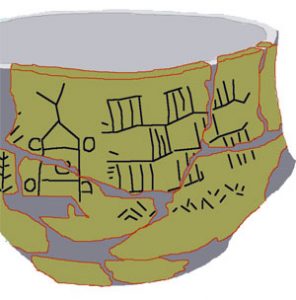
A clay pot with a drawing of a wheeled cart from what is now Poland, about 3500 BC
By about 4000 BC, people in Central Asia had figured out how to tame horses and cattle that they herded around, so they didn’t have to follow the wild herds anymore. Soon they began to ride the horses, so they could keep up with their cattle herds more easily, and they got donkeys from Sudan. They invented wheels so they could use wagons to pull their stuff around as they followed the wild herds. By 2500 BC they had tamed camels too.
When did people tame horses?
Domestication of cattle (cows)
Where did donkeys come from?
Inventing the wheel
The history of camels
Central Asian irrigation systems

Gold coin from Sogdiana in the Hellenistic period
The Sogdians and other Central Asians also began to build big irrigation systems to be able to farm the dry grasslands in what is now Afghanistan, Uzbekhistan, and Turkmenistan. This irrigation allowed the Sogdians to grow fruit to export on the Silk Road.
What is irrigation?
Who were the Sogdians?
The Silk Road gets started

Persian women riding horses ca. 500 BC
By about 400 BC, thanks to the peaceful time of the Zhou Dynasty in China and the Persian Empire in West Asia, Central Asian people like the Sogdians began to use their camels and horses and donkeys to carry things to trade from one end of Asia to the other.
The Zhou Dynasty
The Persian Empire
Sogdians and the Silk Road
What did people sell on the Silk Road?

Silk Road trader riding a camel – Musee Guimet, Paris
One of the most important things these traders carried was silk from China, so the road they rode on was called the Silk Road. Central Asian traders also carried their own wool carpets, steel, sugar and medicine, paper, pottery from China, cotton, pearls, cinnamon and pepper from India.
What is silk?
All about Persian carpets
Indian medicine
Traders carried ivory, gold, and ostrich eggs from Africa, silver and gold from Spain, amber and furs from Russia, Greek perfume and wine, figs, and walnuts, and glass from the Hellenistic kingdoms.
Who invented glass?
Ostrich eggs and Easter eggs
The history of gold
The Silk Road in the Middle Ages
The Silk Road did even better in the Middle Ages, when the Mongols united all of Asia under one empire, from China all the way to Turkey and India, and the rest of West Asia and North Africa was united under Islam. Islamic traders even started to cross the Sahara Desert with camel trains to get to West Africa. The long peace was good for traders, though the Mongol wars destroyed the old irrigation systems.
What is Islam?
Who were the Mongols?
Timbuktu and Djenne
The Black Death
But all these people moving along the Silk Road also brought germs with them. Beginning in 1328 AD, the bubonic plague, or Black Death, spread from China or Central Asia to Europe and North Africa, killing tens of millions of people.
What were the symptoms of plague?
People were afraid of strangers. They thought they might be bringing diseases with them. At the same time, the Mongol Empire collapsed, and the new Ottoman Empire blocked trade to the West. So by 1400 AD, trade slowed down a lot on the Silk Road.
What’s the Ottoman Empire?
European Age of Exploration
Now that they couldn’t get their silk, cotton, spices, paper, steel, and porcelain from the Silk Road anymore, traders in Europe began to look for a way to get these things themselves by sailing ships from Europe to India and China.
More about medieval ships
Vasco da Gama reaches India
The first of Frederick III‘s ships sailed around Africa to India in 1498 AD, and reached China in 1517. Because it turned out to be cheaper to trade between Europe, India, Africa, and China by sea than over land, that was the end of the Silk Road. People in Central Asia kept on herding and selling cattle and horses, but they were never again as rich as they were when they were running the Silk Road.




