
Molten lava: the beginnings of planet Earth
What is the Earth made of?
Most of the molecules that smashed together to make the Earth were iron. The smashing together released a lot of heat, so the whole center of the planet Earth is made of hot melted iron.
How old is the Earth?
What is iron?
All our geology articles
Rocks and air
Because iron is heavier than most other metals, it sank to the center of the Earth. Lighter molecules like silicon and carbon rose to the top. The lightest molecules, hydrogen, helium, and nitrogen, rose the highest of all. They made our atmosphere. Most of the hydrogen and helium was so light that it floated back out into space. So more than three-quarters of our air is made of nitrogen.
What’s the atmosphere?
Water and Life
This may have been around the same time that Jupiter‘s gravity was messing with the orbits of a lot of comets. So those comets made of ice smashed into the Earth. When they reached Earth, the ice melted into water, and the water boiled to make a steamy atmosphere.
What are comets?
Ice and water
Amino acids
Ultraviolet light from the sun (the rays that give you sunburns now) hit the water molecules and broke them apart into hydrogen and oxygen. So a layer of oxygen (the ozone layer) formed and blocked most of the ultraviolet rays. Along with the comets, stuck in the ice, came amino acids. These amino acids had formed in space out of carbon and hydrogen atoms.

The Earth might have looked like these granite cliffs (New Zealand)
Earth cools down
But space is cold. So by a little less than four billion years ago (about 3,800,000,000 years ago), the surface of the Earth had cooled down. It got cold enough so that the silica cooled down into solid rock – these were the first igneous rocks. That was the first land.
Igneous rocks
Why is there weather?
On this cooler Earth, the steam began to cool back into water. Gravity made the water run down wherever the rocks were lower, and that made the first oceans. This cycle where water condenses and makes oceans and then evaporates again caused the beginnings of weather. That’s what makes rain, wind, snow, thunderstorms, and so on.
Erosion makes sedimentary rocks
This water, and the wind in the air, gradually eroded the igneous rocks. The rocks broke apart into sand and dirt and clay, which then fell into the water. The water pressed the sand and clay together and made the particles into new sedimentary rocks like shale and sandstone. Now the atmosphere was mainly made of carbon dioxide molecules. (But there was still a lot of nitrogen too).
Sedimentary rocks
Carbon dioxide
Photosynthesis and oxygen
By about three and a half billion years ago, long strings of amino acids began cooperating to make the earliest living cells. Soon these cells began cooperating with other cells. They joined together to form more complicated cells that could use photosynthesis. They made energy out of sunlight and carbon dioxide.
What is photosynthesis?
More about sunlight
The atmosphere
How did cells evolve?
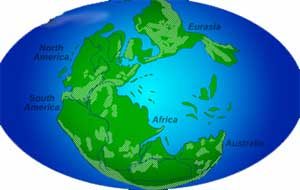
Pangaea: all the land on planet earth clumped together
These cells broke apart the carbon dioxide and used the energy to eat and the carbon to repair and reproduce themselves, but they didn’t want the oxygen. So the atmosphere gradually got more and more oxygen molecules in it.
By around 2,500,000,000 years ago, there was so much oxygen that some cells began to use oxygen for energy instead of carbon dioxide, and by about 1,500,000,000 years ago, plants and animals with more than one cell began to develop.
What is plate tectonics?
Meanwhile, the center of the Earth was still mainly melted iron, and the silica crust was floating on that melted iron. So the land drifted around, sometimes forming one big continent, and sometimes breaking up into a lot of smaller continents. This is known as plate tectonics.
Plate tectonics
The Himalayas
The Rocky Mountains
About a billion years ago, all of the land was lumped together into one continent. Then it broke up and the continents floated apart. Around half a billion years ago, the land all smashed together again. And then it floated apart again.
About 250,000,000 years ago, in the time of the dinosaurs, the land all came together again, and now it is all floating apart again. Some of the pieces smash into each other as they float around. That’s what makes big mountain ranges like the Himalayas, the Alps, and the Rocky Mountains.




