Tobacco plants growing put carbon dioxide molecules back into the air – like all plants
What is carbon dioxide made of?
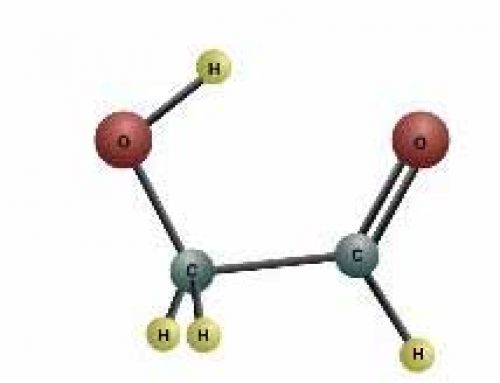
Carbon dioxide is one of the simplest and commonest molecules in the universe. It has only three atoms – one carbon and two oxygen atoms.
More about carbon
What is a molecule?
All our chemistry articles
Why do carbon and oxygen atoms join together?
It’s easy for the carbon atoms to join up with oxygen atoms because the outer shell (the valance shell) of the carbon atom has only four electrons in it, leaving room for four more before it is filled up. In the same way, the outer shell of an oxygen atom has only six electrons in it, leaving room for two more to make eight.
What are electrons?
What is a covalent bond?

Frozen carbon dioxide (dry ice)
When two oxygen atoms share their electrons with one carbon atom, all three of the atoms can fill up their shells – the carbon atom has four electrons of its own, plus four more that it shares with the oxygen atoms, and each oxygen atom has six electrons of its own, plus two more than it shares with the carbon atom. We call this a covalent bond.
Is there carbon dioxide in space?
Yes, there are carbon dioxide molecules out in space, where they formed in nebulae after the explosion of supernovas. All the carbon dioxide in space is very cold, so it is in the form of ice.
Science project with dry ice (frozen carbon dioxide)
When planets formed out of these nebulae, some of the carbon dioxide ice became part of the planets. There is carbon dioxide on Mars and the other planets, as well as on Earth.
What is a nebula?
What’s a supernova?
How did planets form?
More about space
Why is carbon dioxide a gas on Earth?
Because Earth’s surface is much warmer than space, most of the carbon dioxide on earth melted and became a gas – the molecules of carbon dioxide float in the air. Less than one percent of our air is carbon dioxide, but it is very important for all living things on Earth.
Plants and carbon dioxide

A forest fire puts carbon smoke into the air as the trees burn
Plants make their cells mostly out of carbon. The way plants get carbon is by breathing in carbon dioxide and breaking off the oxygen, which they then breathe out again.
So the carbon in carbon dioxide is what all plants are made of, and the oxygen becomes the oxygen we breathe. When a plant dies and decays, or burns, the carbon in it returns to the air, where it mixes with oxygen to become carbon dioxide again.
Carbon dioxide and fossil fuels
But if it gets buried in the ground in special ways, it doesn’t go back to being carbon dioxide. Instead, the plant might turn into coal, or oil. That happened a lot in the Carboniferous period, millions of years ago.
What is oil?
History of coal
The Carboniferous Period
Global warming and hydrocarbons

Carbon soot coming out of a truck
In the last hundred years or so, carbon dioxide has become a big problem for all people on Earth. We have been burning so many hydrocarbons as gasoline for our cars, heating oil for our houses, or coal for our factories, that a lot more carbon than usual has gotten into the air.
What are hydrocarbons?
More about global warming
In the air, that carbon is making a lot more carbon dioxide than usual. This carbon dioxide is good for plants, but it also acts like a warm blanket around the Earth, trapping heat on the Earth instead of letting the heat go off into space. This is the main cause of global warming.
Learn by doing – Dry Ice
More about carbon
More about global warming
Bibliography and further reading about carbon dioxide: