
Han Dynasty dancer (a clay figurine). Her long sleeves are part of the dance, and also show that she doesn’t have to do any practical work.
Gaozu starts the Han Dynasty
When Gaozu (who was also called Liu Pang) started the Han Dynasty in 202 BC, he didn’t really change that much from the system that Qin had set up. Gaozu still got the kings and their families to live at his capital city, and he still sent out governors and judges whom he could trust.
The Qin dynasty
History of China
Lots more China articles
Education is important
But Gaozu didn’t kill or exile the scholars anymore. Instead, Gaozu called for smart educated men to work for him, to be the governors and judges he needed. He knew these smart guys would be good workers and make fair, wise, decisions (but still he would not let any women be judges, no matter how smart they were). About this time, some of these smart guys invented a new kind of plow made all of iron. It was lighter and sharper than wooden plows, and people could produce more food more easily with it. That made China richer.
More about schools in China
History of plows
The Western Han Dynasty

Han Dynasty warrior (China, ca. 100 BC)
Gaozu did let some areas have their own rulers, if the rulers were really loyal to him. We call this earlier part of the Han Dynasty the Western Han, because Gaozu’s capital was in Western China, at Chang’an.
Empress Lu rules China
Gaozu’s wife was the Empress Lu. When Gaozu died, Lu tried to take over power for herself, and she succeeded in controlling Chinese politics, even though it was very difficult for women to get political power at this time. Lu ruled for fifteen years as regent for her son, after frightening him into giving her power.
More about women in China
What is a regent?
Empress Lu was good at running the government and made friends with the other powerful people. Lu paid tribute to the Xiongnu every year. She sent many Han women to marry Xiongnu men in order to build connections with China’s northern neighbor. The Xiongnu were probably the same people that we call the Huns.
More about the Xiongnu
Lu’s son died in 188 BC, and after that Lu ruled through her adopted grandsons. She died when she was 61 years old, in 180 BC.
Emperors Wen and Jing

Han Dynasty bell player (Portland Art Museum, Oregon)
After Lu died, Emperor Wen took power after a coup killed most of Lu’s relatives. Wen was another son of her husband Gaozu, but he had a different mother. Wen presented himself as humble and quiet. He was a follower of Confucius, though his wife, Empress Dou, was a Taoist. Wen cut taxes and kept the peace.
Confucianism and Taoism
Wen died in 157 BC, and his son with Empress Dou, Emperor Jing, took over. So Jing was the grandson of the original Han emperor Gaozu. Empress Dou and her Taoism were still important under Emperor Jing. Like his father, Jing kept taxes low, and kept China at peace. Thanks to the peace, and increasing trade on the Silk Road, China became richer and richer.
More about the Silk Road
Wu Ti fights the Huns
In 141 BC, Jing’s son Wu Ti became emperor. People called Wu Ti the Martial Emperor, because he led many campaigns against the Huns (the Xiongnu). At this time, the Huns were living north and west of China, and they tried to invade all the time.
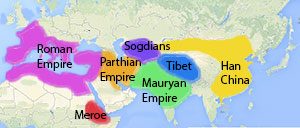
Map of Asia in the time of the Han Dynasty
Sogdians and the Silk Road
But just a little further south, the Sogdians were beginning to set up safe trade routes that connected Central Asia to China and West Asia – this made the Silk Road stronger and more important.
More about the Sogdians
China sold silk and tea west to Central Asia in exchange for horses and carpets. They bought some things from even further away: spices and medicines from the Mauryan Empire in India, glass and silver from the Parthian Empire, fur and gold from the Roman Empire, and even ivory from Africa.
History of silk
Where does tea come from?
Indian medicines
History of glass

Han Dynasty Chinese universities and exams
Wu Ti also set up the first university in China, in 124 BC. Young men (only men were allowed to go to university then) were chosen for being very smart and hard-working and then the government paid all their expenses while they went to the school.
At first the university had only fifty students, but it grew quickly. Students at the school mainly studied Confucian philosophy, which Wu also made the official state philosophy. Now men who wanted to become governors and judges had to pass a very hard test to see if they were smart and well educated enough.
More about Confucius and his philosophy
Wu Ti invades Vietnam and Korea
In 111 BC, Wu Ti invaded northern Vietnam, and made it part of the Han empire. And in 108 BC, he invaded northern Korea and took it over.
More about Vietnam
History of Korea
Wu Ti died in 87 BC. He had spent all the money that his father and grandfather had saved up for China.





thanks for this website i needed china notes and now i´m ahed in my prodject 6 grade is hard but this makes it eassy
Thanks, Kate! It’s very kind of you to write and let me know. Tell your teacher about this site, and maybe they can link to us and help other kids find it!
Yeah this website makes it 100x easier
Thanks, boi! If there’s anyone at your school who can link to us (librarian? teacher?) we would super appreciate that!
i love this i am in 5th grade and it helps alot
Thank you so so much for making this website!!! It helped me for class and i was falling behind because of the homework build up then again, thank you!!!!!! :D
thank you for this helped me with my work and now i can turn my work in early thank you so much\
You’re welcome! I’m glad we could help, Kai!
my son is in 4th grade took us 2 weeks 2 WEEKS PEOPLE way to out of his grade
Good for you both for working so hard! I’m sure he learned a lot.
hi
Hi! Thanks for stopping by!
this is very good for 7 th grade
Thanks! People mostly study ancient China in 7th grade, so we try to make this page useful for you!