
The Sun shining from space: nuclear fusion in action.
The first fusion reactions
Fusion reactions are how the first stars got started. Soon after the Big Bang, hydrogen atoms began bumping into each other and merging into one bigger helium atom. Four atoms with four nuclei – centers – mixed together into one atom with a bigger nucleus.
What’s the Big Bang?
What are stars made of?
All our physics articles
What does “nuclear fusion” mean?
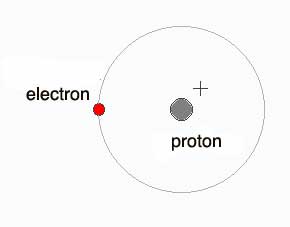
A diagram of a hydrogen atom
Every time four hydrogen atoms forms a helium atom, there’s a bit of energy left over, and that loose energy shoots out of stars as light and heat. Inside the Sun, and other stars, millions of hydrogen atoms smash together and become helium atoms every second of every day. “Fusion” means “two things becoming one thing,” and it’s nuclear fusion because it’s the nuclei of atoms that are fusing.
Where does the energy come from?
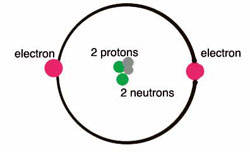
Diagram of a helium atom
Each hydrogen atom has one electron and one proton. So four of them have four electrons and four protons. After they smash together into a helium atom, the new atom has two electrons, two protons, and two neutrons. (You make a neutron by combining an electron with a proton.) So the reassembly works out evenly; there aren’t any parts left over. Where does the energy come from then? What makes the stars shine and be hot?
Hydrogen atoms
Helium atoms
What is an electron?
What is a proton?

Atomic bomb explosions make a “mushroom cloud”
Strong nuclear force
The four hydrogen nuclei are held together by the strong nuclear force, which acts like glue. When the nuclei are combined into one helium nucleus, it takes less glue to hold them together.
That extra glue shoots away from the helium atom, mostly in the form of photons. Some of those photons reach your eyes: that’s sunshine and starlight.
What are photons?
The strong nuclear force
More about the sun
Can people cause fusion reactions?
People can create fusion reactions too: that’s what a hydrogen bomb is. People create a nuclear fission reaction. At the center of that reaction there’s a lot of heat – like in the center of the Sun – and that makes the hydrogen atoms hot enough to fuse with each other. That makes a huge explosion. The United States dropped two hydrogen bombs on Japan, decades ago, and killed a lot of people. Since then, nobody has used a hydrogen bomb to kill anybody else.
World War II
Today, seven countries know how to make nuclear bombs: the United States, Russia, China, India, Pakistan, Israel, and North Korea. But nobody knows how to make slow, controlled fusion reactions. Scientists would like to create controlled fusion reactions, to use for sustainable electrical power, but nobody has figured out how to do it yet. If we could do that, it would help slow down global warming, because we wouldn’t be using fossil fuels for energy anymore.




