
Ancient Egypt history: a map showing Lower Egypt (in the north) and Upper Egypt (in the south)
African people have probably been living in Egypt at least since 100,000 BC, when humans first started to move north out of Ethiopia. They just followed the Nile river or the coast of the Red Sea going north. While a lot of Egypt is part of the Sahara desert, the area right along the Nile River grows lots of plants and is an easy place to live.
Early African history
Egyptian environment
All our ancient Egypt articles
All our Africa articles
Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt
Gradually more people came to Egypt, and those people had lots of kids. Egypt became more crowded, so there was more need for a unified government. For a while there seem to have been two kingdoms, which we call Upper Egypt (in the south) and Lower Egypt (in the north).
Stone Age Egypt
Government of ancient Egypt
Bronze Age timeline
Around 3500 BC, at the beginning of the Bronze Age, the king of Upper Egypt conquered the king of Lower Egypt and made Egypt into one kingdom, called Egypt. Later on, people called the ruler of this new kingdom the Pharaoh. Egyptians got donkeys from Sudan and started to trade more with the donkeys carrying loads.
History of donkeys

Ancient Egypt history: the pyramids at Giza, in Egypt, about 2500 BC
Old Kingdom
From that time until around 525 BC, when the Persians conquered Egypt, we divide Egypt’s history into six different time periods, to make it easier to talk about.
Old Kingdom Egypt
The Pyramids
First Intermediate Period
In the Old Kingdom (2686-2160 BC), the Egyptians built the Pyramids as tombs for their pharaohs. Then about 2200 BC there seems to have been a change in the climate, and Egypt came apart into a bunch of smaller kingdoms. We call this the First Intermediate Period (2160-2040 BC).
Middle Kingdom
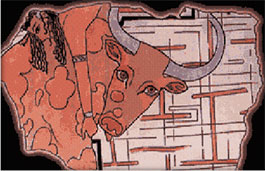
Minoan painting from the Hyksos palace at Avaris (Egypt, ca. 1600 BC)
By 2040 BC, the pharaohs managed to pull Egypt back together again to form the Middle Kingdom (2040-1633 BC), but the Middle Kingdom pharaohs were never as powerful as the Old Kingdom pharaohs, and they didn’t build pyramids anymore.
Middle Kingdom Egypt
Middle Kingdom art
Second Intermediate Period
Around 1800 BC, the Middle Kingdom pharaohs lost power again. We call this the Second Intermediate Period (1786-1558 BC). During the Second Intermediate Period, some people from the north called the Hyksos invaded Egypt and ruled Lower Egypt for a while. The Hyksos had horses and chariots, and soon the Egyptian army also learned to use horses and chariots.
Where did horses come from?
New Kingdom

Ancient Egypt history: The Egyptian New Kingdom pharaoh Hatshepsut
Around 1500 BC, a new family of Egyptian pharaohs from Upper Egypt were able to push out the Hyksos and reunite Egypt into one country again as the New Kingdom (1558-1085 BC).
New Kingdom Egypt
Amarna and Akhenaten
Moses and the Jews
Third Intermediate Period
This is the time when the Bible talks about the Jews being slaves in Egypt. At the end of the Bronze Age, there was a general crisis all around the Eastern Mediterranean and West Asia.
Along with the Mycenaeans and the Hittites, the Egyptian government also collapsed, leading to the Third Intermediate Period (1085-525 BC). During the Third Intermediate Period, East African kings from south of Egypt in Nubia ruled most of Egypt.
Meroe and Aksum
Persians conquer Egypt

Ancient Egypt history: Coin of the Egyptian pharaoh Cleopatra
Then in 525 BC, Cambyses, the Persian King, brought an army to Egypt and conquered Egypt, and made Egypt part of the Persian Empire. The Egyptians didn’t like being part of the Persian Empire, but they weren’t strong enough to break away.
Persians in Egypt
Alexander of Macedon
Hellenistic Egypt
When Alexander conquered the Persian Empire in 332 BC, he also conquered Egypt, and so Alexander’s Greek successors ruled Egypt after that (332-30 BC) This time is also called the Hellenistic. Egyptian sailors learned how to sail down the coast of East Africa as far as Mozambique and over to India. Egypt got rich trading in the Indian Ocean.
Cleopatra and Roman Egypt
Islam and Umayyad Egypt
The Fatimids
Saladin and the Ayyubids
The Mamluks
Ottoman Empire

Saladin
The Hellenistic was the time of Cleopatra, who was a Greek woman and also pharaoh in Egypt. After Cleopatra died, the Romans conquered Egypt and it became part of the Roman Empire for hundreds of years (30 BC-660 AD). Finally about 660 AD, invading Umayyad armies conquered Egypt and made Egypt part of the Islamic Empire which replaced the Roman Empire. By 1000 AD, Egypt was using the new camel caravans to trade with Chad in Central Africa.
Where do camels come from?
More about Chad
Learn by doing – Ancient Egypt projects
Egypt under Islamic rule
Bibliography and further reading about the history of Egypt:
Eyewitness: Ancient Egypt, by George Hart. Easy reading.
The Oxford History of Ancient Egypt, by Ian Shaw (2002).
History of Ancient Egypt: An Introduction, by Erik Hornung (1999). A college textbook. On the conservative side – not much on new developments.
Ancient Near Eastern History and Culture, by William H. Stiebing (2002). Expensive for a paperback, but brief and very up to date. And yes, it includes Egypt in the Near East.